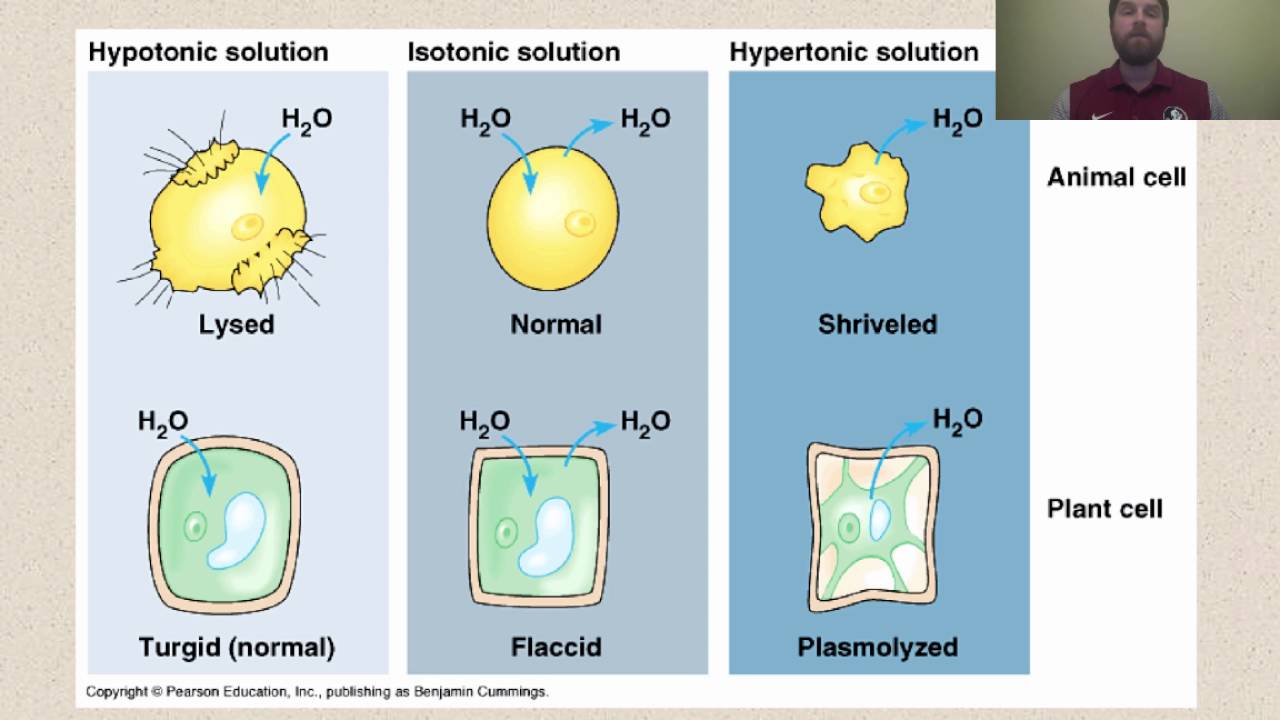
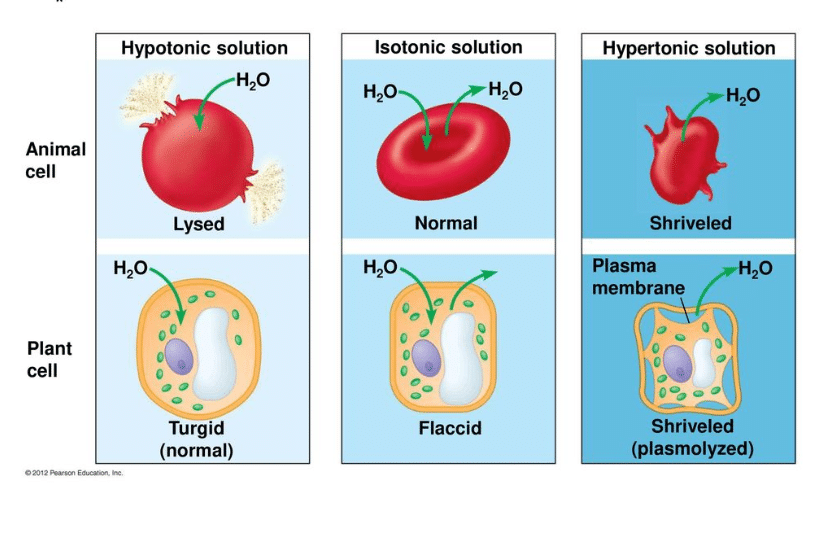
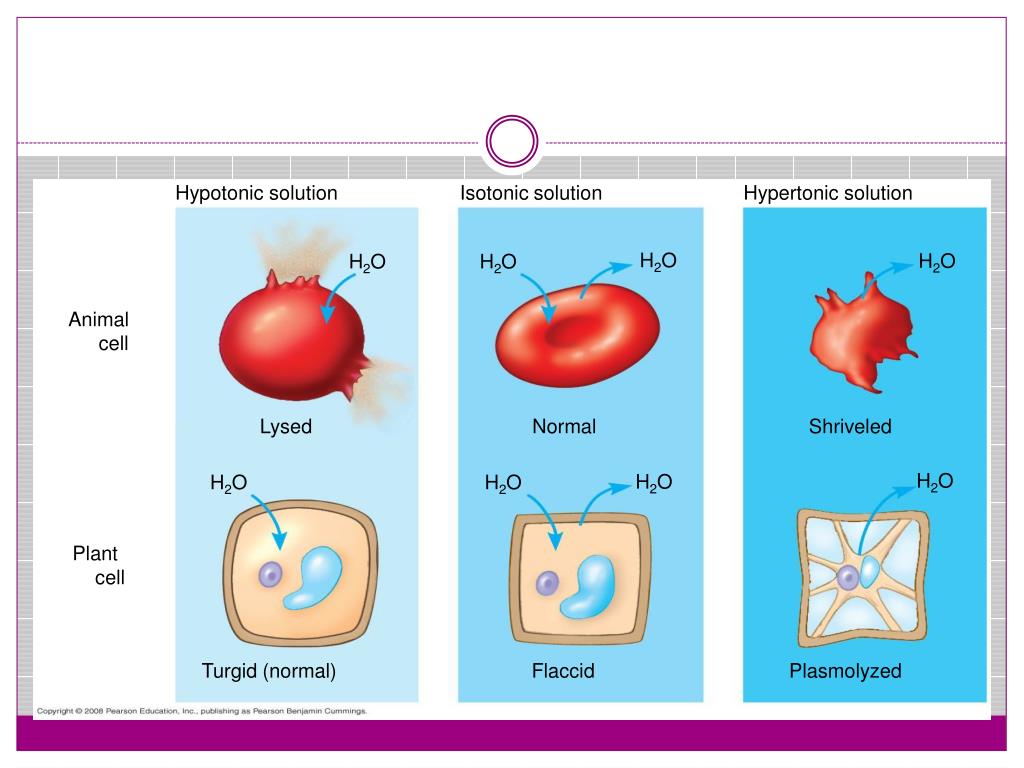
A cell in a hypotonic solution will. If you place an animal or a plant cell in a hypertonic solution, the cell shrinks, because it loses water ( water moves from a higher concentration inside the cell to a lower concentration outside ).
Biology Flipclass for 111115 on The Cells' Environment a
When viewed under a microscope, the vacuoles of plant cells appear noticeably larger.
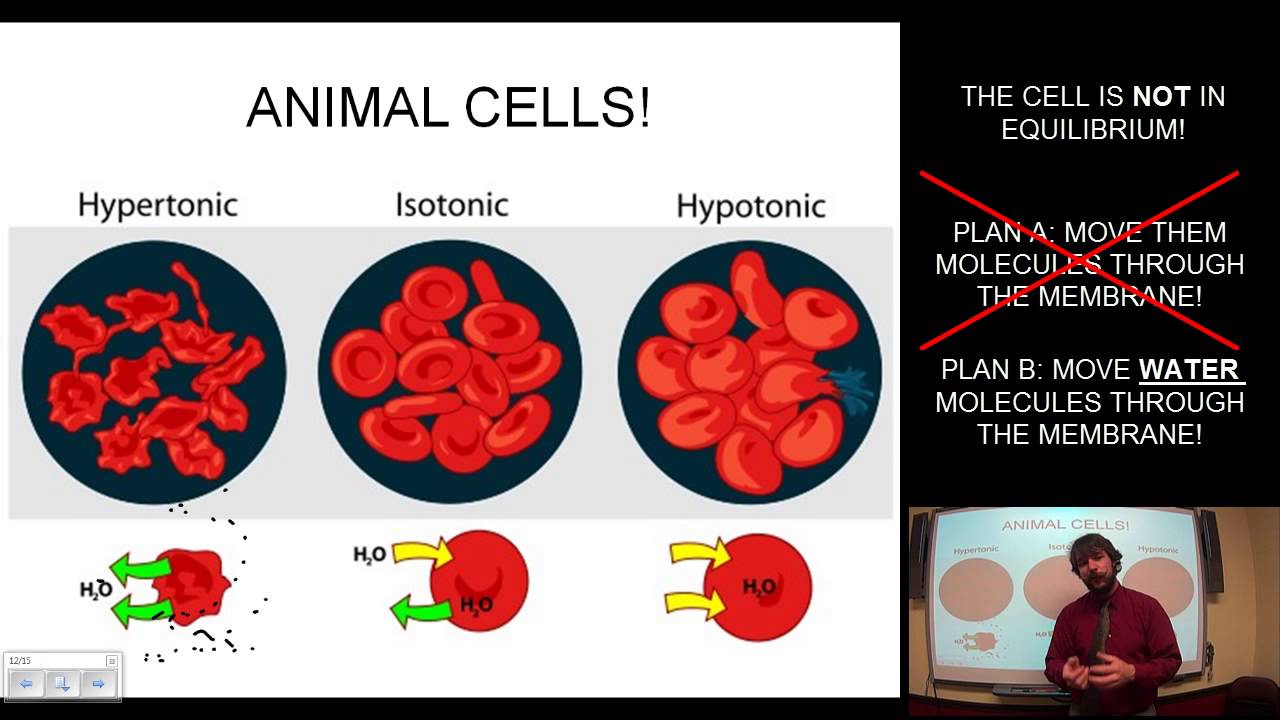
Animal cell placed in hypertonic solution. In this case, water will leave the cell since the cell has a lower osmolarity than the extracellular fluid. In this case, that is the inside of the cell. Osmosis draws water out of the solution and into the cells.
If enough water is lost, the cell will take on a wrinkled or. Alternatively, if a cell is placed in a hypertonic solution, the cell will shrink due to the movement of water outside the cell through osmosis. An animal cell placed in a hypertonic solution will shrink in a process called crenation.
Therefore, a hypertonic solution has more solutes than the intracellular environment, so water will leave the cell to try to achieve equilibrium. A cell in an isotonic solution will. What happens to a cell placed in a hypertonic solution and why?
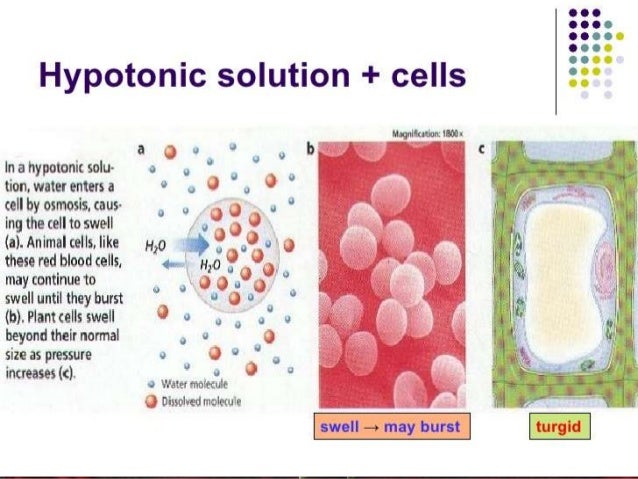
Hypotonic solutions a solution is hypotonic to a cell if it has a lower solute concentration than the cell does. As a result, it also has a higher concentration of water than the cell does. A single animal cell ( like a red blood cell) placed in a hypotonic solution will fill up with water and then burst.
What happens when a plant cell is placed in a hypotonic solution? When a cell is placed in a hypotonic environment, water will enter the cell, and the cell will swell. As a result, plant and animal cells both appear more plump when placed in a hypotonic solution.
The electrical activity of these cells relies on the positive and negative charges of the ions in the hypertonic solution. A single animal cell ( like a red blood cell) placed in a hypotonic solution will fill up with water and then burst. Pressure decreases to the point where the protoplasm of the cell peels away from the cell wall, leaving gaps between the cell wall and the membrane and making the plant cell shrink and crumple.
If a cell is placed in a hypertonic solution, water will leave the cell, and the cell will shrink. Due to exosmosis, both animal and plant cells will shrink. What happens when you place an animal cell in a hypertonic solution?
When an animal cell is placed in a hypertonic solution, water diffuses across the. If a plant cell is placed in a hypertonic solution, the plant cell loses water and hence turgor pressure by plasmolysis: For a discussion about what happens to a cell in a hypertonic solution, ‘solution’ refers to the extracellular environment.
In an isotonic environment, there is no net water movement, so there is no change in the size of the cell. What will happen if an animal cell is placed in hypertonic solution ? A cell in a hypotonic solution may gain enough water to lyse, or rupture, the cell membrane, which destroys the cell.
If the solution has the same solute concentration, and thus the same water concentration, as the cells do, it is isotonic to the cells. An animal cell has very small vacuoles but no rigid cell wall, a pliable and fluid cell membrane surrounds it. Hypotonic solution examples diagram what is a hypotonic solution video lesson transcript study com from study.com if you place an animal or a plant cell in a hypertonic solution, the cell shrinks, because it loses water ( water moves from a higher.
If you place an animal or a plant cell in a hypertonic solution, the cell shrinks, because it loses water ( water moves from a higher concentration inside the cell to a lower concentration outside ). Animal cells, especially nerve cells, rely on a hypertonic solution and the ions in it to create an action potential or nerve signal. To prevent crenation or hemolysis, an animal cell must be placed in an isotonic solution such as 0.9% (m/v) nacl or 5.0% (m/v) glucose.
Water is stored in the vacuole causing it to expand and exert pressure on the cell wall. When an animal cell, such as a red blood cell, loses water to the hypertonic solution, it shrinks, or crenates. If animal and plant cells are kept in hypertonic solution then exosmosis will occur.
When a cell is placed in a hypertonic (more concentrated) solution water. The cells were placed in a hypotonic solution. An animal cell placed in a hypotonic solution will swell and potentially burst in a process called hemolysis.
When placed in a hypertonic solution, the plant cell will lose water from its vacuole and the cell wall will draw inwards until or if equilibrium is reached. When a cell is placed in hypotonic solution, water enters the cell through osmosis. Exosmosis is a process in which the water molecules move from inside of the cell of lower solute concentration to the outside of the cell of higher solute concentration through the cell membrane.
What happens to a cell in a hypotonic solution quizlet? A sample of cells is placed in a salt solution. A hypertonic solution is less concentrated compared to the cytoplasm of the animal cell.
The difference between a hypotonic solution and a hypertonic solution is tabulated below: As a result the cell would shrink in what is called plasmolysis. As a result, plant and animal cells both appear more plump when placed in a hypotonic solution.
When a animal cell is placed in a hypotonic solution. Cell burts because water diffuses into cell. A single animal cell ( like a red blood cell) placed in a hypotonic solution will fill up with water and then burst.
A hypotonic solution has less solute concentration and more solvent concentration. This is why our bodies work to maintain homeostasis, so that the blood and tissue fluid surrounding our cells will be isotonic (equal concentration of dissolved solutes and water) to the cells. An animal cell that is placed in a hypotonic solution will rapidly gain water, because osmosis would cause the water to move to an area with more solutes.
A cell placed in a hypotonic solution will swell due to the movement of water into the cell. Hyper is a latin prefix meaning over or above. If the concentration difference is great enough, the cells can die.
What happens to plant and animal cells in hypertonic hypotonic and isotonic solutions?
Hypertonic solution causes cells to shrink and shrivel up

Uncategorized Anna Scott's AP Biology Blog

Hypotonic, Isotonic, Hypertonic Solution Effect On Cells
PPT introducing Osmosis PowerPoint Presentation ID2087870
The effects of hypotonic, hypertonic and isotonic
What Happens When A Cell Is Placed In A Hypotonic Solution
An Animal Cell Placed In A Hypertonic Solution Will Blank
What happens to animal cells kept in a Hypertonic solution
What is an isotonic solution and why would it be used in

Effects of Osmosis on Cells Structure and function, Cell
What Is A Hypotonic Solution Get Education
What are some examples of hypotonic and hypertonic
PPT Practical Biology Biol 101 Lab 6 PowerPoint

hypertonic + isotonic + hypotonic solutions Animal cell

Enlighten yourself with Diffusion and osmosis Biology360

07 membrane structure and function