They may have distinct top and bottom sides. Most animals living in the sea exhibit radial symmetry.
Symmetry in Animals Types of Symmetry, Bilateria and
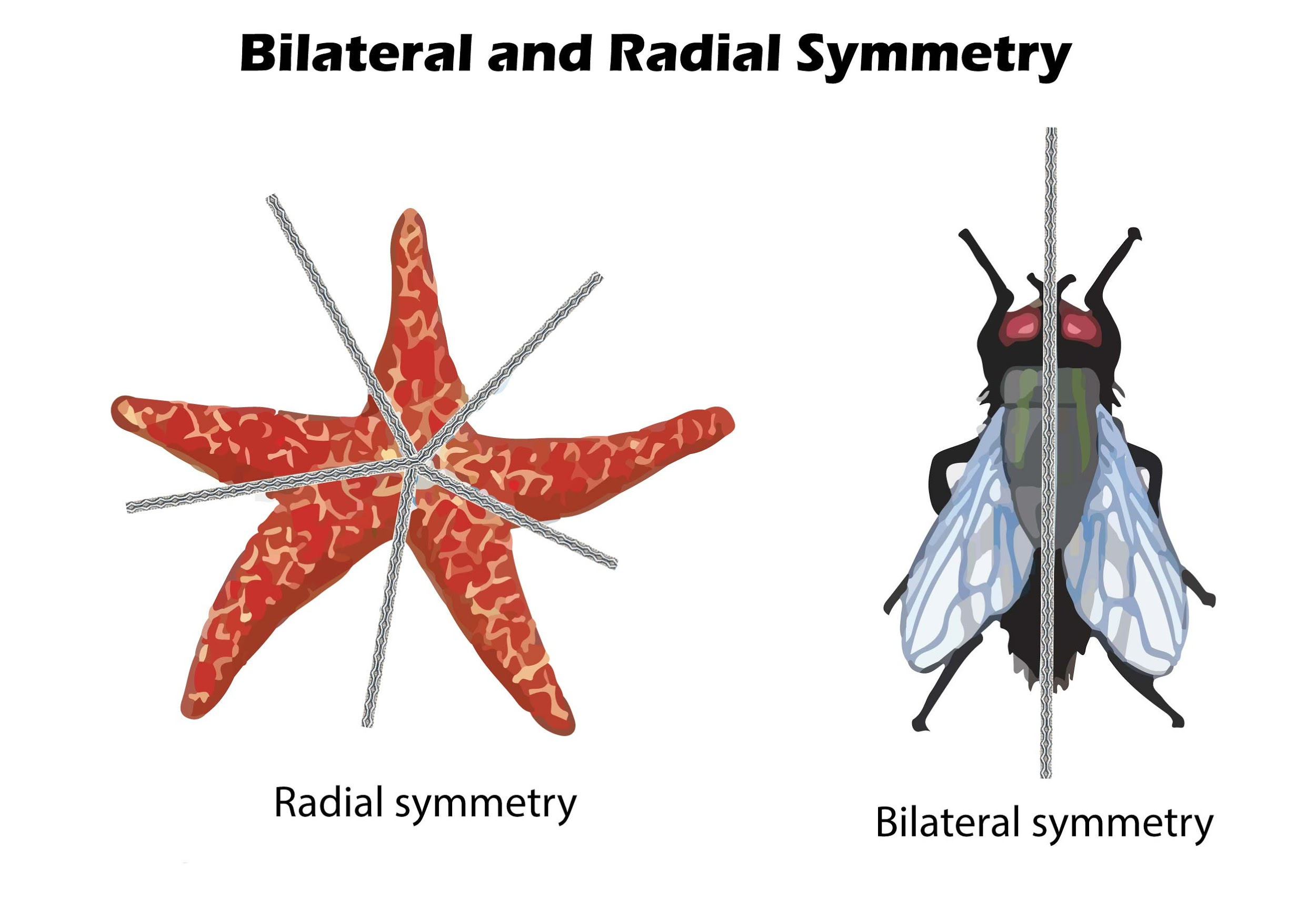
Examples of animals with radial symmetry are jellyfish, sea urchins, and sea stars.the bodies of most animals can be divided into equal left and right halves along the central axis and this is known as bilateral or mirror symmetry.
Radial symmetry animals. Is a jellyfish radial or bilateral? For sessile (sedentary) organisms, radial symmetry is useful because the animal can just “sit down” and grab food or detect threats from all directions. Despite the diversity within the jellyfish clade, medusozoa, all 200 described jellyfish species exhibit radial symmetry.
Corals build colonies that are not symmetrical, but the individual polyps exhibit radial symmetry. Animals in the phylum echinodermata (such as sea stars, sand dollars, and sea urchins) display radial symmetry as adults, but their larval stages exhibit bilateral symmetry. The radial symmetry is present in aquatic animals,.
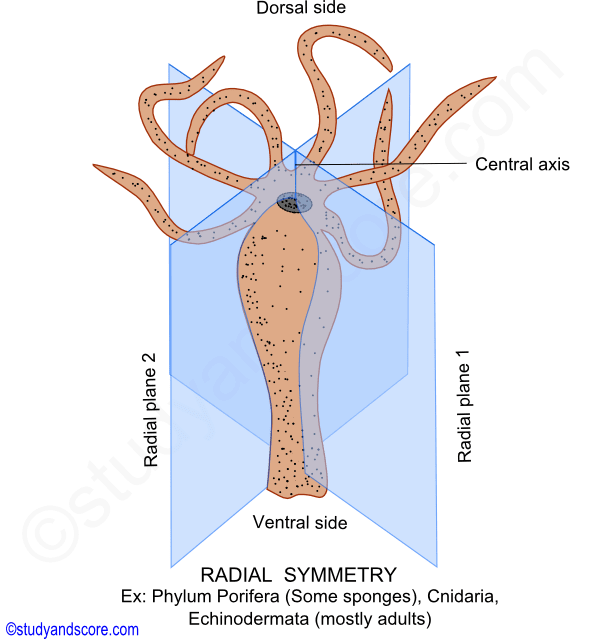
Radial symmetry is found in the cnidarians (including jellyfish, sea anemones, and coral) and echinoderms (such as sea urchins, brittle stars, and sea stars). In the animal kingdom, there are two broad phyla that exhibit radial symmetry: Any line drawn from one side through the center to the opposite side will divide the animal into two symmetrical halves.
Because of the circular arrangement of their parts, radially symmetrical animals do not have distinct front or back ends. Radially symmetric animals are mostly symmetric about their axis. Radially symmetrical animals have top and bottom surfaces, but no left and right sides, or front and back.
Radial symmetry the arrangement of parts in an organ or organism such that cutting through the centre of the structure in any direction produces two halves that are mirror images of each other. Some animals with radial symmetry are starfish, sea anemone, and jellyfish.some animals with bilateral symmetry are frogs, lizards, all mammals. Sessile animals like sea anemone, slow moving organisms like starfish and floating animals like jellyfish are examples of radially symmetrical animals.
Radial symmetry is found in sessile organisms such as floating organisms and echinoderms, such as sea stars and sea urchins. Most radially symmetric animals are symmetrical about an axis extending from the center of the oral surface, which contains the mouth, to the center of the opposite (aboral) end. Radial symmetry is advantageous to sedentary organisms because sensory receptors are evenly distributed around the body.
Symmetry in animalsin this video, you will learn about two types of symmetry, radial, and bilateral symmetry.animals with radial symmetry are circular in sha. Radial symmetry is usually, echibited in animals whichclass:12subject: What is radial symmetry in animals?radial symmetry is the arrangement of body parts around a central axis, like rays on a sun or pieces in a pie.
Jellyfish exhibit radial symmetry in four. Asymmetry if an organism can’t be placed in the groups above, it is said to be asymmetric. Cnidaria and echinodermata animals are also considered as radially symmetric.
Radial symmetry is a very rare characteristic seen in animals and organisms, as opposed to bilateral symmetry. Radial symmetry an organism has radial symmetry if it can be divided into thirds, fourths, fifths and so on, by passing a plane at any angle along a central axis. Sessile animals such as sponges are asymmetrical.
Sea anemone, starfish and jellyfish respectively. This is termed secondary radial symmetry. One of these is cnidarians , which include jellyfish, anemones, and corals.
Other than animals, plants also exhibit the radial symmetry. How can radial symmetry be a benefit to an animal? Radial symmetry is applicable for an animal if it has an up and down orientation, which implies any plane cutting the animal in the longitudinal axis produces equal halves on both sides.
Alpheidae feature asymmetrical claws that lack pincers, the larger of which can grow on either side of the body, and if lost can develop on the opposite arm instead. Symmetry in organismal biology radial and bilateral for example, many radial animals are sessile forms or plankton images of symmetry in the animal. Animals with radial symmetry have many lines of symmetry.
Animals with radial symmetry have many lines of symmetry. People, dogs, cats, and elephants all have bilateral symmetry. The stems and roots of plants usually show radial symmetry, while all animals belonging to the cnidaria (e.g.
Radial symmetry has some special forms like tetrameric, pentamers, hexamers, and octamers. 3 animals with radial symmetry have body parts arranged around a central point. Some examples of these animals are jellyfish, sea urchins, corals, and sea anemones.
Animals in the phyla cnidaria and echinodermata generally show radial symmetry, [7] although many sea anemones and some corals within the cnidaria have bilateral symmetry defined by a single.

Radial Symmetry When an organism can be divided at any
Are there animals that actually have a line of symmetry

Features Used to Classify Animals Boundless Biology

12 best Animal characteristics images on Pinterest
PPT Animal Systems PowerPoint Presentation ID2725836
/87145409-57c472725f9b5855e5bab697.jpg)
Radial Symmetry in Marine Life
Made by Teachers Animals With Radial Symmetry Get Information

Radial Symmetry The Definitive Guide Biology Dictionary
Radial symmetry occurs in aFishes bMolluscs CStarfishes

The common sea urchin has radial symmetry. (Paracentrotus
PPT INVERTEBRATES About 97 percent of all animals are
Radial Symmetry by noraneko DPChallenge

Sciency Thoughts A possible bilaterally symmetrical

24 best images about radial symmetry on Pinterest Sun
Biology Final 2010 65 Animal with radial symmetry
What is the reason humans and animals have a leftright

An animal with radial symmetry can be divided into two