Growth is restricted to the tips of stem and roots. Animal tissue refers to the group of cells of similar structure and function in animals.

Plant and Animal Tissues YouTube
Examples of plant tissues include:

Examples of plant and animal tissues. For more detailed information about plant and animal tissues, visit byju’s. Meristematic tissue (apical meristem, intercalary meristem, lateral. These tissues were the first to evolve during evolution and were first formed during embryonic development.
Embryonic tissue embryonic tissue can be divided into two kinds of stem cells: This process of taking up a permanent shape, size, and function is called differentiation. Epithelial tissue covers the outer surface of the body and internal organs.
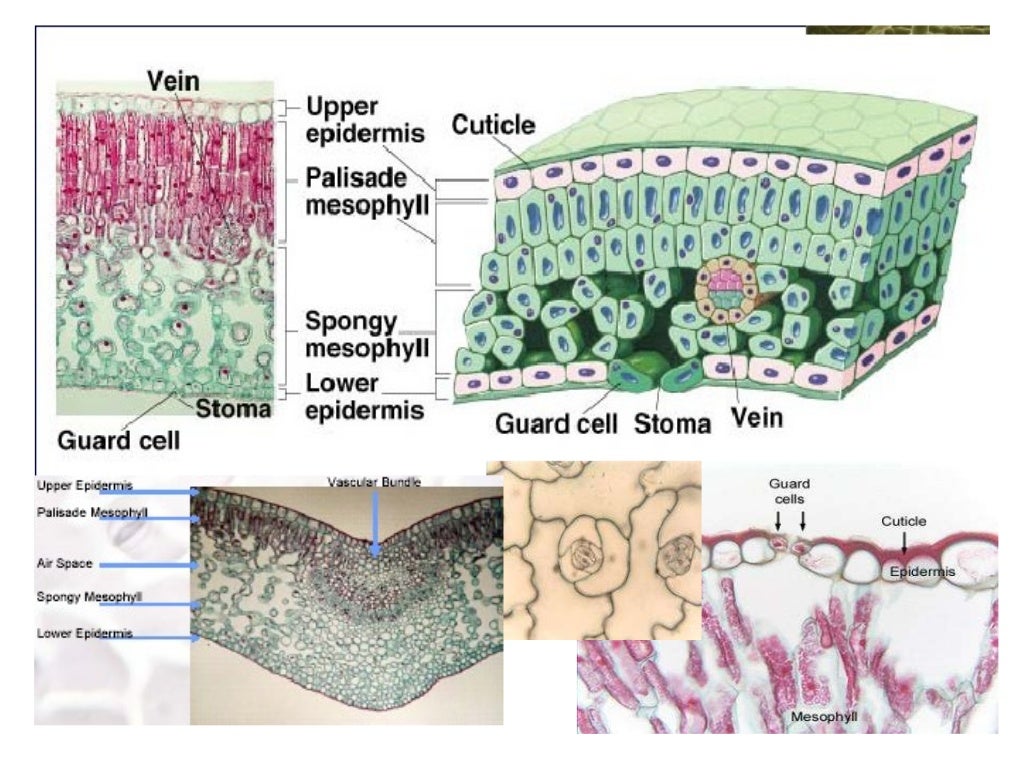
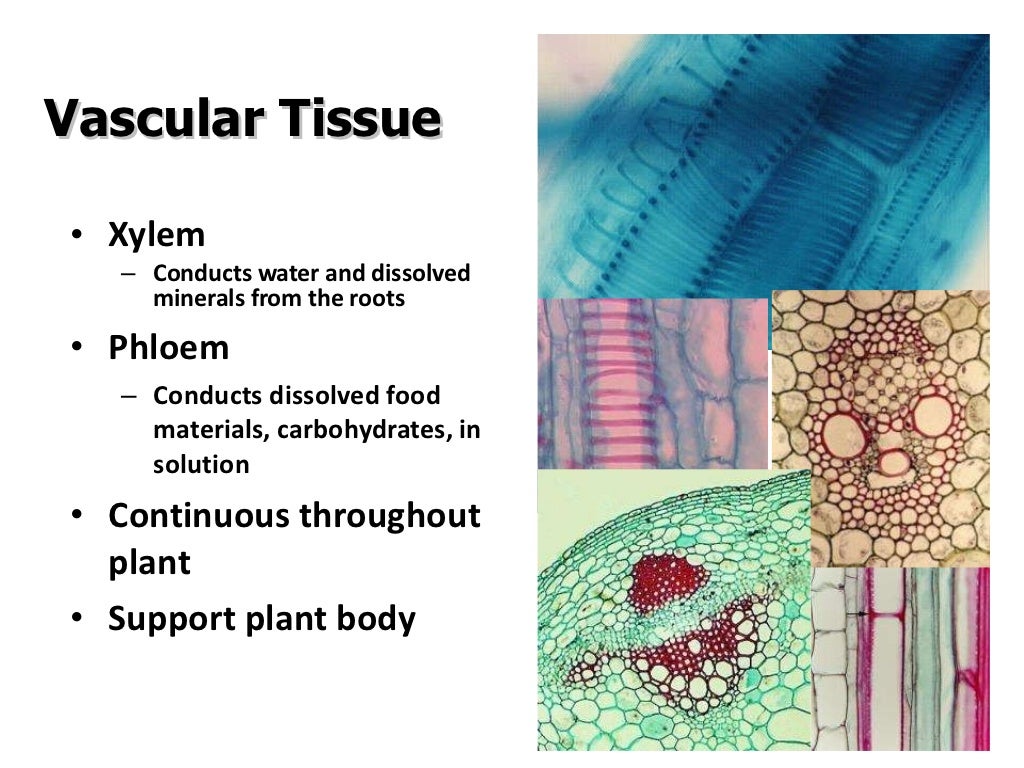
The epidermis, the ground tissue, and the vascular tissue. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. Some examples of specialised tissue types 6.1 plant epidermis 6.2 xylem 6.3 animal cartilage and bone 6.4 epithelia 6.5 nervous tissue glossary bibliography biographical sketches summary
These are generally restricted to certain regions. Lateral meristems occur in woody trees and plants. An organ is made from two or more tissues, which all work together to do a particular job, like the heart in animals or a leaf in a plant.
According to this classification, there are two types of plant tissues. Neurons and glia.the main function of nervous tissue is the processing of information coming from the external and internal environments, and then. An organism is composed of tissues, which are made up of individual cells.
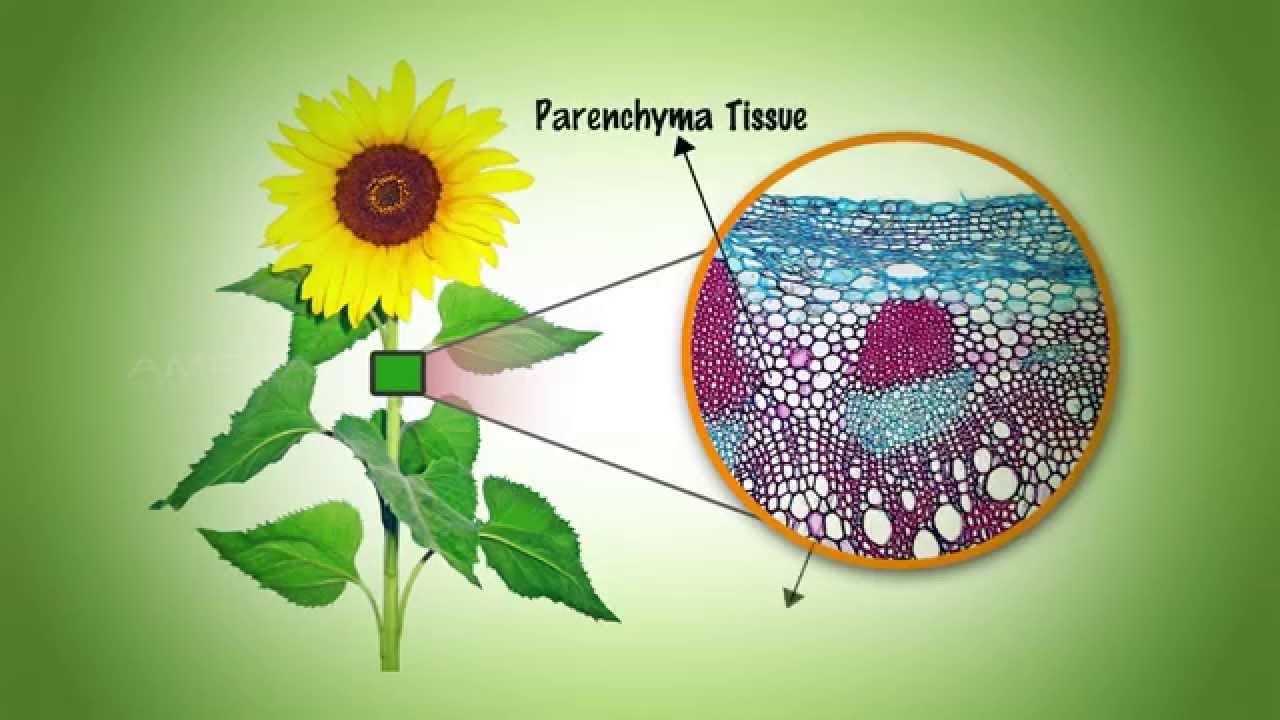
Two types of permanent tissues are found in plants i.e. For example, millions of muscle cells make up muscle tissue. In plant anatomy, tissues are categorized broadly into three tissue systems:
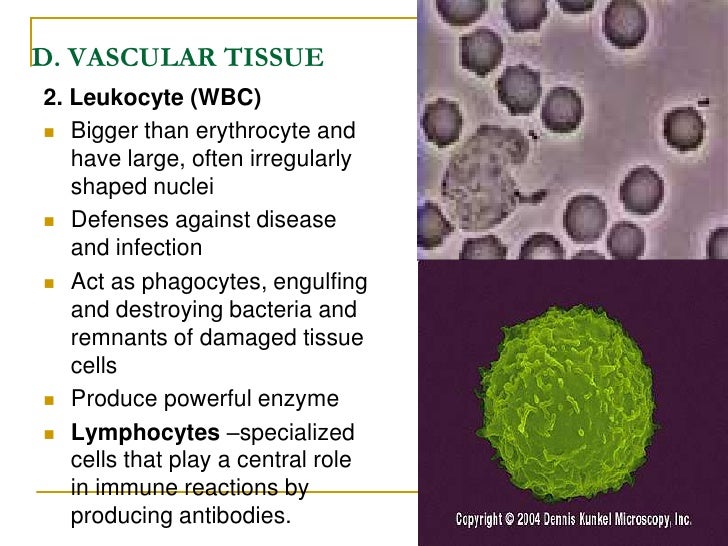
The nervous tissue is composed of two cell types: Therefore the body shows many. Cells of animal tissue do not have cell wall.
Animal tissue animal cells with the same structure and function are organised into tissues. Start studying plant and animal tissues. These transport fluids and nutrients internally.
Lateral meristematic tissue make the plant grow thicker. The different types of animal tissues include: Examples of lateral meristematic tissue include the vascular cambium that results in the rings you see in trees, and cork cambium or 'bark' found on.
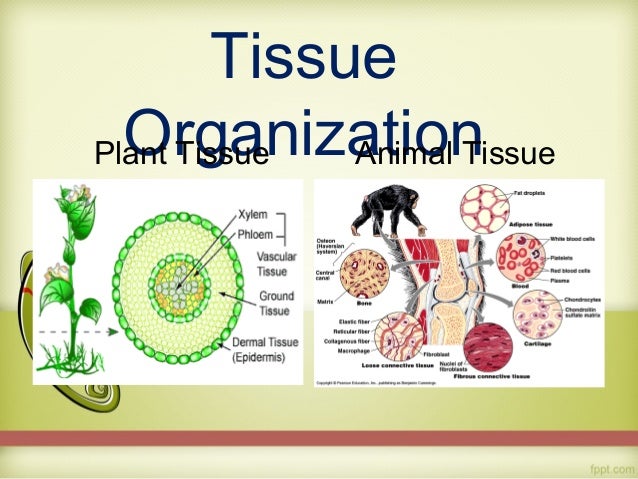
(1) pith, (2) protoxylem, (3) xylem, (4) phloem, (5) sclerenchyma, (6) cortex, and (7) epidermis are the different plant tissues. Simple permanent tissues include parenchyma, collenchyma, and sclerenchyma while complex tissues are xylem and phloem. The three fundamental tissue patterns seen in roots and stems that serve to distinguish between woody dicot, herbaceous dicot, and monocot plants are an excellent illustration of this.
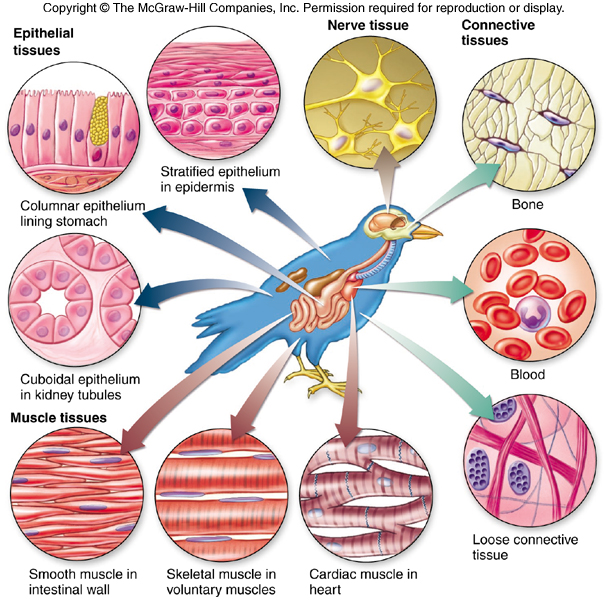
Illustrate and describe how tissues are organized in the regions of the plant organ c. 7 rows the table gives some examples of animal and plant tissues. Epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscle tissue and nerve tissue.
Growth is uniform all over the body. Therefore we can aptly differentiate the plant tissues on the basis of the dividing capacity. Animal tissues nervous tissue n ervous tissue develops from the embryonic ectoderm, the layer covering the embryo that becomes the epidermis.
Simple and complex permanent tissue. Various plant tissues are important ingredients in traditional medicine. Examples of animal tissues are:
Present in animal or plant. Recognize variations of each of the different tissues in different organs. A tissue is a group of cells having a common origin, similar structure and function and held together by a cementing substance.
Illustrate, describe, and differentiate the various types of tissues characteristic of vascular plants b. Some tissues are living and some are dead. Cells of plant tissue have cell wall.
Epithelial tissue, muscle tissue, connective tissue, neural tissue. Animals move from one place to the other in search of food, shelter etc. Learn plant and animal tissues & get access to important questions, mcq's, videos & revision notes of icse class 7 biology chapter at topperlearning.
General organisation of tissues 5.1 tissue systems in plants 5.2 animal extracellular matrix (ecm) 6. Xylem, phloem, parenchyma, collenchyma, sclerenchyma, epidermis and meristematic tissue. 4.4 vessel elements in plants 5.
They are mainly of two types permanent tissue and meristematic tissue. A cell is the basic structural and functional unit of a living organism. They are of four types muscle tissue, epithelial tissue, nervous tissue and.
Epithelial tissues form the protective covering and inner lining of the body and organs. It is of the following types: They develop from the ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm of the embryo.
BIOLOGICAL SCIENCEplant and animal tissues
Plant and Animal Tissues MeitY OLabs YouTube
BIOLOGICAL SCIENCEplant and animal tissues
Difference between Plant Tissues and Animal Tissues CBSE
Presentation03 Plant and Animal Tissues
Presentation03 Plant and Animal Tissues

Study of plant and animal tissues from chars and prepared
Plant And Animal Tissue authorSTREAM

Presentation03 Plant and Animal Tissues

Tissue Definition and Examples in Biology Scienza

Presentation03 Plant and Animal Tissues

Animal tissues Plant and animal tissues Siyavula

Animal Tissues Animal Tissues Class 11 CBSE +1 Biology
6biopinos PLANT AND ANIMAL TISSUES